Trees play a pivotal role in maintaining the health and balance of our environment. From improving air quality to conserving water, trees offer numerous environmental benefits that help to sustain ecosystems, combat climate change, and enhance our quality of life.
As urbanisation and deforestation continue to rise, planting more trees has become an essential practice for preserving the environment.
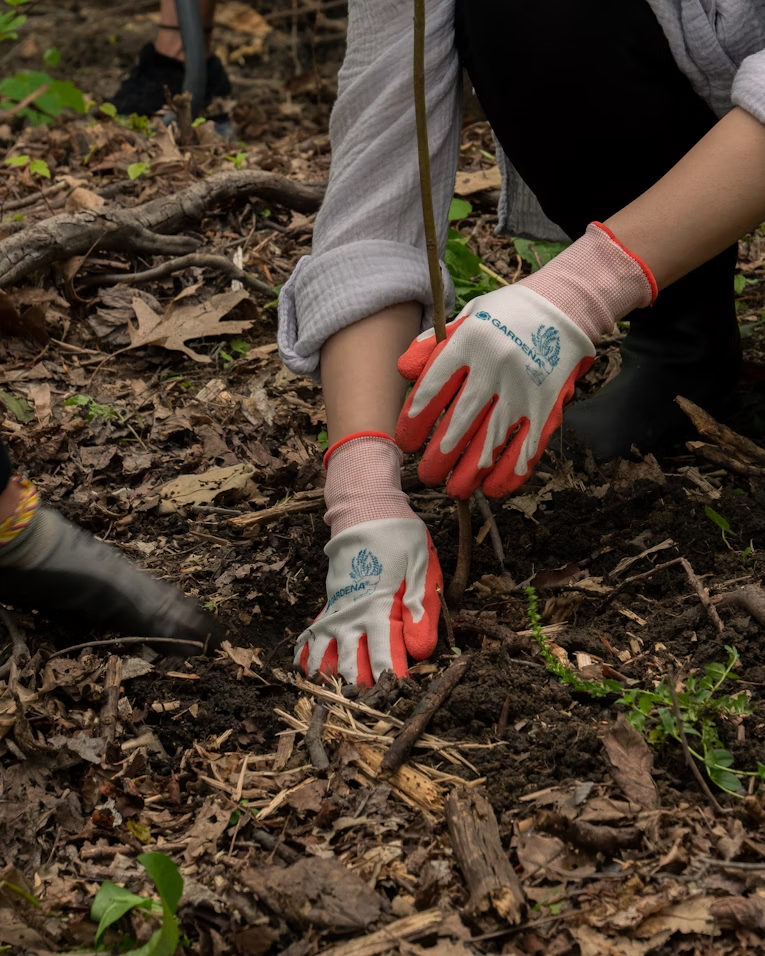

In this article, we will discuss the many environmental advantages of planting trees and why it is more important than ever to integrate trees into our landscapes.
If you’re looking to make your outdoor space more sustainable, consider planting more trees like Harry’s Yard, a great place to start your green initiative.
The Role of Trees in Reducing Carbon Footprint
One of the most significant environmental benefits of planting more trees is their ability to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2), a major greenhouse gas contributing to climate change.
Trees help mitigate the effects of climate change by removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass. This process, known as carbon sequestration, helps to reduce the overall carbon footprint.
1. Trees Absorb Carbon Dioxide
Every year, millions of tonnes of carbon are released into the atmosphere due to human activities like burning fossil fuels.
Trees act as natural carbon sinks, removing CO2 from the air through photosynthesis. By planting more trees, we can increase the amount of CO2 being absorbed and stored, thus reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases.
How Carbon Sequestration Works:
Photosynthesis
Trees absorb CO2 through their leaves and convert it into oxygen and glucose, which fuels their growth.
Storage in Biomass
The absorbed carbon is stored in the tree’s roots, trunk, branches, and leaves, keeping it out of the atmosphere.
Long-term Storage
Trees store carbon for as long as they are alive, and even after they die, their carbon content can remain in the soil for extended periods.
2. Reducing the Urban Heat Island Effect
In urban environments, the increased concentration of buildings and infrastructure can create heat islands, where temperatures are higher than in surrounding rural areas.
Trees help mitigate this effect by providing shade and cooling the environment through a process called transpiration, where moisture from leaves evaporates into the air, cooling the surrounding area.
Trees Improve Air Quality
Trees also contribute to cleaner air by removing pollutants from the atmosphere. They absorb gases like nitrogen oxides, ammonia, and sulphur dioxide, and filter particulates such as dust, ash, and smoke.
As a result, planting trees can directly improve air quality, making the environment healthier for humans and wildlife alike.
1. Filtering Pollutants
Trees are highly effective at filtering the air. Through a process called biofiltration, trees capture harmful pollutants on their leaves and bark, preventing them from entering the atmosphere.
Pollutants Trees Remove:
Nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Found in vehicle emissions, these gases contribute to the formation of smog.
Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
This gas, produced by industrial activities, can cause acid rain and respiratory issues.
Particulate matter
Trees capture airborne particles such as dust, pollen, and soot, improving air quality.
2. Reducing Respiratory Illnesses
By improving air quality and reducing the concentration of harmful pollutants, trees help to reduce the risk of respiratory illnesses such as asthma and bronchitis. Communities with abundant green spaces and trees often have lower rates of these conditions.
Conserving Water with Trees
Water conservation is another key environmental benefit of planting more trees. Trees help regulate the water cycle, prevent soil erosion, and reduce water runoff, making them an essential part of water management strategies.
1. Reducing Water Runoff
Urban areas with little vegetation often experience high levels of water runoff during rainfall, leading to flooding and water pollution. Trees absorb rainwater through their roots and allow it to gradually seep into the soil, reducing runoff and decreasing the likelihood of flooding.
2. Preventing Soil Erosion
The roots of trees stabilise the soil and prevent it from being washed away by heavy rainfall. This is especially important in areas prone to flooding or erosion. By planting trees, we can protect the land and maintain the integrity of local ecosystems.
Enhancing Biodiversity and Wildlife Habitats
Trees are a crucial part of the ecosystem, providing shelter and food for countless species of wildlife. From birds to insects and small mammals, trees offer essential habitats and help maintain biodiversity.
1. Providing Habitats for Wildlife
Trees are vital habitats for many species, including birds, insects, and mammals. They provide nesting sites, food sources, and shelter for animals, helping to sustain biodiversity and support healthy ecosystems.
Types of Wildlife Supported by Trees:
Birds
Trees provide shelter and nesting sites for birds, such as parrots, finches, and woodpeckers.
Insects
Trees support insect populations by offering food sources (e.g., pollen and nectar) and habitats for pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Small Mammals
Trees provide shelter and food for small mammals such as squirrels, possums, and bats.
2. Promoting Pollination
Many trees, especially flowering varieties, provide essential resources for pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. By planting trees, we can support pollinator populations, which are critical for maintaining plant diversity and crop production.
How Trees Help Pollination:
- Flowering trees: Trees like cherry blossoms, magnolias, and acacias provide nectar and pollen, supporting pollinators.
- Biodiversity support: Pollinators that rely on trees also help fertilise other plants in the area, supporting the overall health of the ecosystem.
The Role of Trees in Combating Climate Change
In addition to their ability to absorb carbon, trees help combat climate change in several ways. Through their role in the water cycle, soil conservation, and providing habitat for wildlife, trees contribute to the resilience of ecosystems against the effects of climate change.
1. Carbon Storage
The carbon stored in trees remains out of the atmosphere, reducing the overall concentration of greenhouse gases. This makes trees one of the most effective tools in the fight against climate change.
How Trees Store Carbon:
- Long-term carbon storage: Trees store carbon in their wood, roots, and leaves, acting as a long-term carbon sink.
- Mitigating climate change: As trees grow, they absorb and store more carbon, helping to slow down the rate of global warming.
2. Creating Climate Resilient Landscapes
By planting trees, we create more resilient landscapes that are better equipped to handle the effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events, floods, and droughts. Trees play an essential role in regulating temperature and improving the overall health of the ecosystem.
Conclusion
The environmental benefits of planting more trees are clear. From reducing carbon emissions and improving air quality to conserving water and enhancing biodiversity, trees play a critical role in creating a sustainable and healthy environment.
By planting more trees, we can combat climate change, improve our quality of life, and contribute to the overall health of the planet.
Whether you’re enhancing your garden or planting trees in your community, every tree planted has a positive impact. Consider taking action today and start planting trees to help create a greener, healthier world.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do trees help reduce global warming?
Trees help reduce global warming by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and storing it in their biomass. This process lowers the overall concentration of greenhouse gases in the air, mitigating climate change.
What types of trees are best for carbon sequestration?
Fast-growing and long-living trees, such as eucalyptus, oak, and pine, are excellent for carbon sequestration due to their ability to absorb large amounts of CO2 and store it over time.
How can trees conserve water in urban areas?
Trees conserve water in urban areas by reducing runoff, improving water absorption, and stabilising soil. This helps prevent flooding and ensures that rainwater is absorbed into the groundwater supply, rather than running off into stormwater systems.